- At the core of every link-state routing protocol is a distributed, replicated database.
- The database describes the following:
- The routing topology > the collection of routers routing in the routing domain.
- How each router interconnects.
- Each router in the routing domain is responsible for describing its local piece of the routing topology in “link-state advertisements or LSAs.”
- LSAs are “reliably” distributed to all routers in the routing domain in a process called reliable flooding.
- The collection of LSAs generated by all routers is called the “link-state database.”
- The flooding algorithm ensures that each router has an identical link-state database, except during brief periods of convergence.
- When the network is in a “steady state,” which means that no routers or links are going up and down.
- The only OSPF routing traffic is periodic hello packets between the neighbors and the occasional refresh of pieces of the link-state database.
- Hello packets are usually sent every 10 seconds, and failure to receive hellos from a neighbor tells the router of a problem in its connected link or neighboring router.
- Every 30 minutes, a router refloods the pieces of the link-state database that it is responsible for, just in case those pieces have been lost or corrupted in one of the other router’s databases.
Link State Advertisements (LSAs)
- Each OSPF router originates one or more LSAs to describe its local part of the routing domain.
- All OSPF LSAs start with a 20-byte common header, which carries a “record.“
OSPF Header

The major fields of the OSPF packet header are as follows:
- Version—OSPF version number, which is 2 for OSPFv2.
- Type—OSPF packet type from 1 to 5, corresponding to hello, DD, LSR, LSU, and LSAck, respectively.
- Packet length—Total length of the OSPF packet in bytes, including the header.
- Router ID—ID of the advertising router.
- Area ID—ID of the area where the advertising router resides.
- Checksum—Checksum of the message.
- AuType—Authentication type, ranging from 0 to 2, corresponding to non-authentication, simple (plaintext) authentication, and MD5 authentication, respectively.
- Authentication—Information determined by authentication type. It is not defined for authentication type 0. It is defined as password information for authentication type 1 and defined as Key ID, MD5 authentication data length, and sequence number for authentication type 2.
Identifying LSAs
- OSPF LSAs are identified by three fields found in the common LSA header:
- LS Type
- Link State ID
- Advertising Router
LSA Type Field –
The LS Type field broadly classifies LSAs according to their functions. Five LSA types are defined by the base OSPF specification.
LSA Type 1 – Router LSA
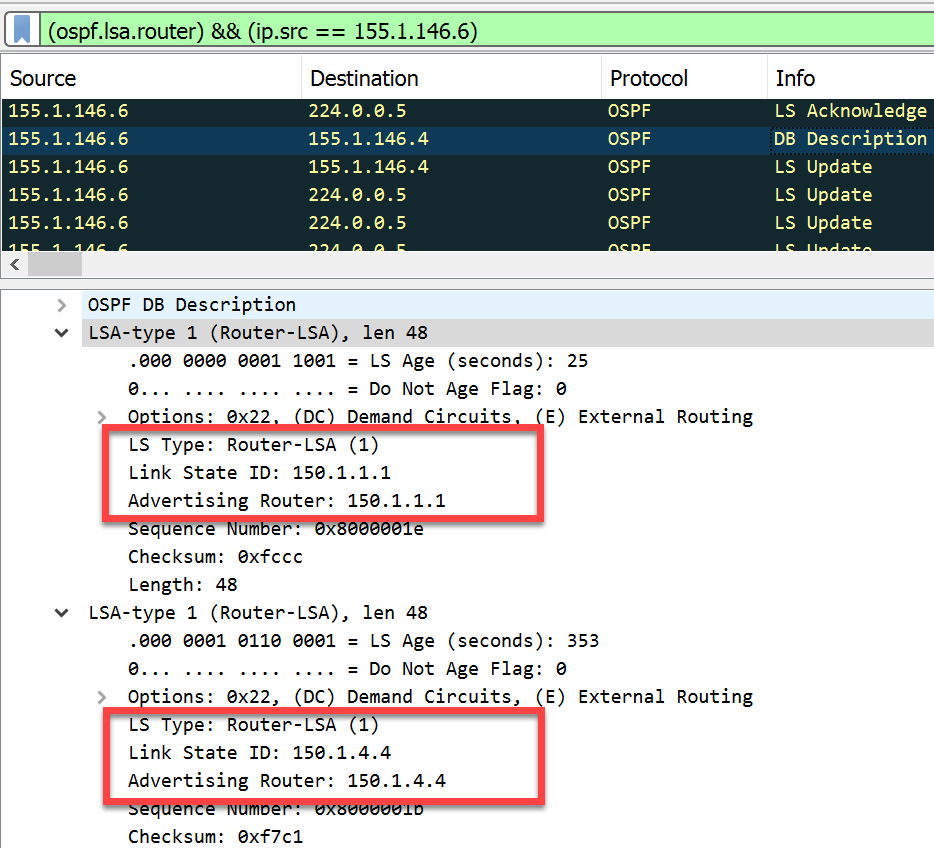
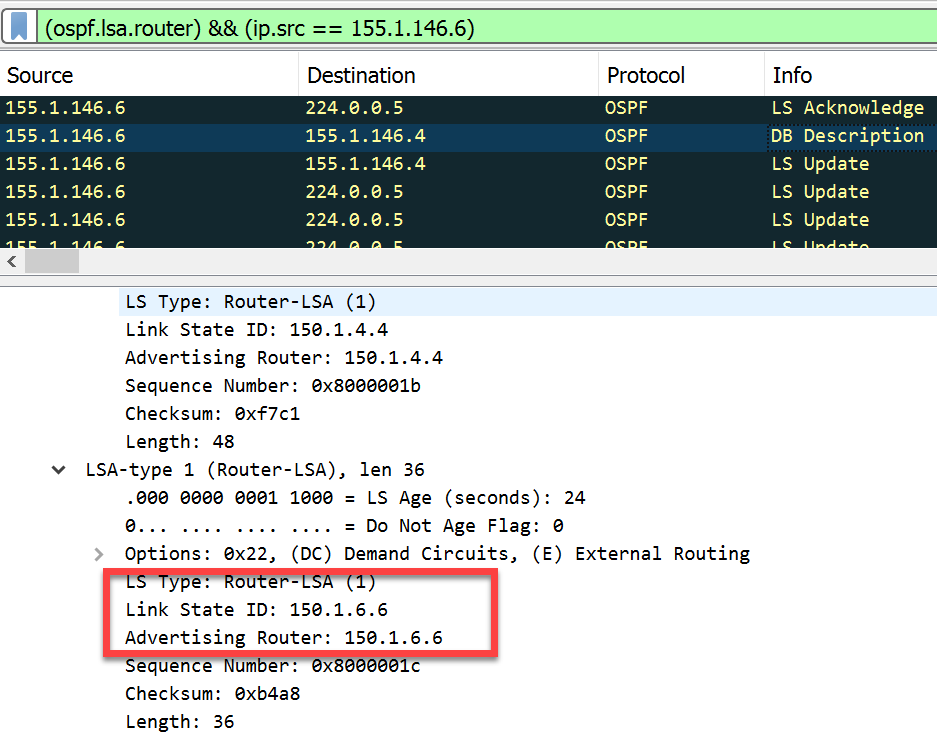
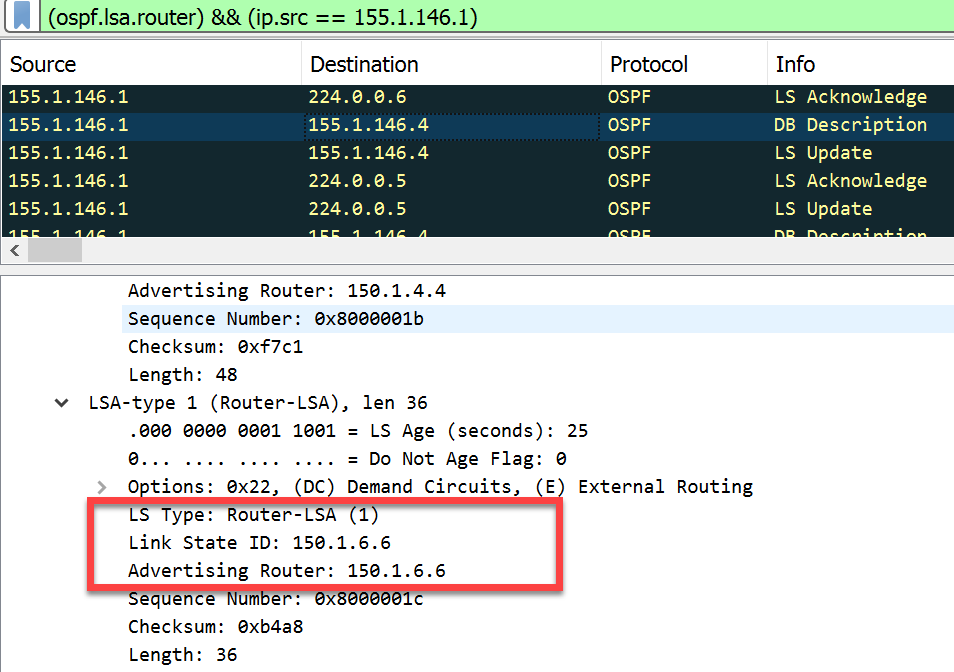
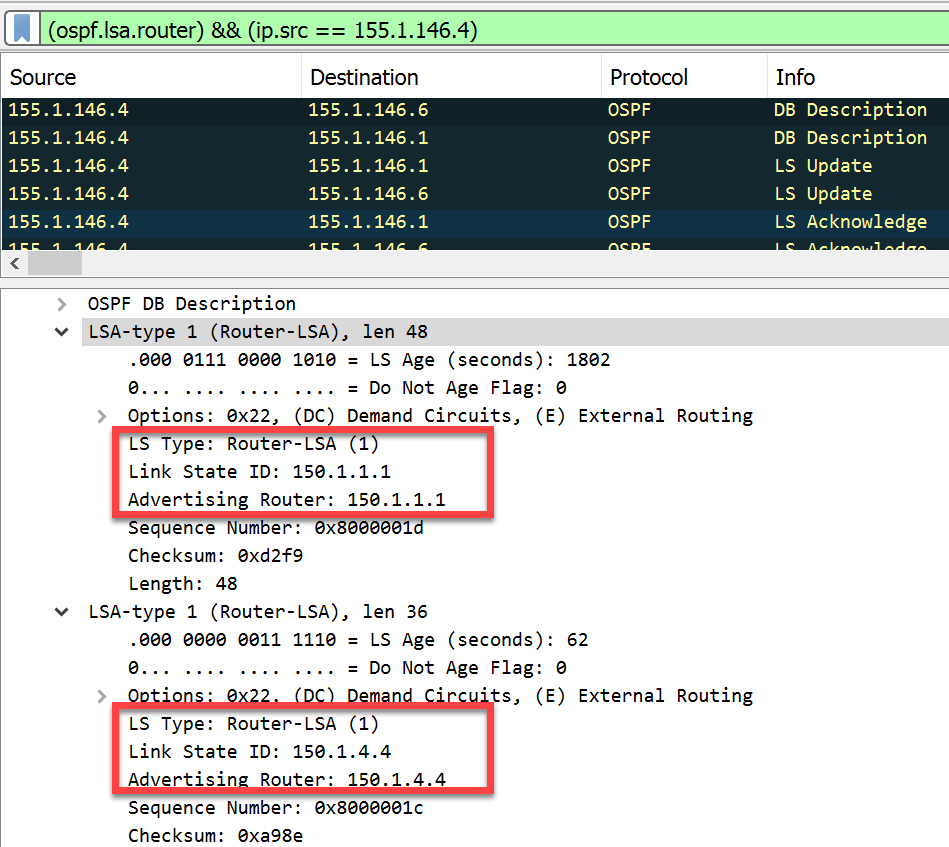
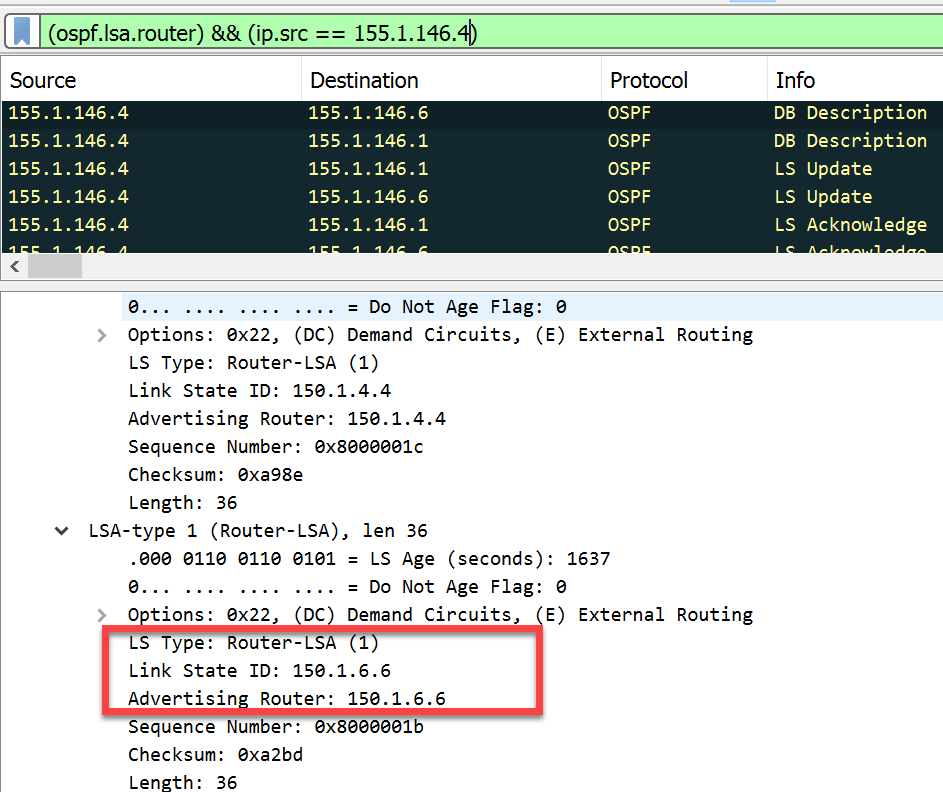
- Router LSAs > Each router originates a single router LSA to describe its set of active interfaces and neighbors.
- In a routing domain with point-to-point links, the link-state database consists only of router LSAs.
- Link State ID: In a Type 1 LSA, the Link State ID field is set to the router’s own ID. This allows other routers in the area to recognize the LSA as belonging to that particular router.
- SPF Tree Calculation: Type 1 LSAs are crucial in the OSPF Shortest Path First (SPF) tree calculation process. Routers use information from Type 1 LSAs to calculate the shortest path to reach destinations within the OSPF area.
In summary, Type 1 LSAs (Router LSAs) are essential components of OSPF routing protocol. They provide information about a router’s interfaces and their states, allowing OSPF routers to build and maintain an accurate network topology within an OSPF area. This information is critical for calculating the shortest paths to reach destinations and ensuring efficient routing in OSPF networks.
OSPF Database of R1, R4 and R6
R1
R1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (150.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
150.1.1.1 150.1.1.1 9 0x80000020 0x00CCFC 2
150.1.4.4 150.1.4.4 10 0x8000001F 0x00EFC5 2
150.1.6.6 150.1.6.6 10 0x8000001E 0x009CC0 1R1#show ip ospf 1 database network
OSPF Router with ID (150.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Net Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 1855
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Network Links
Link State ID: 155.1.146.4 (address of Designated Router)
Advertising Router: 150.1.4.4
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x7E07
Length: 36
Network Mask: /24
Attached Router: 150.1.4.4
Attached Router: 150.1.1.1
Attached Router: 150.1.6.6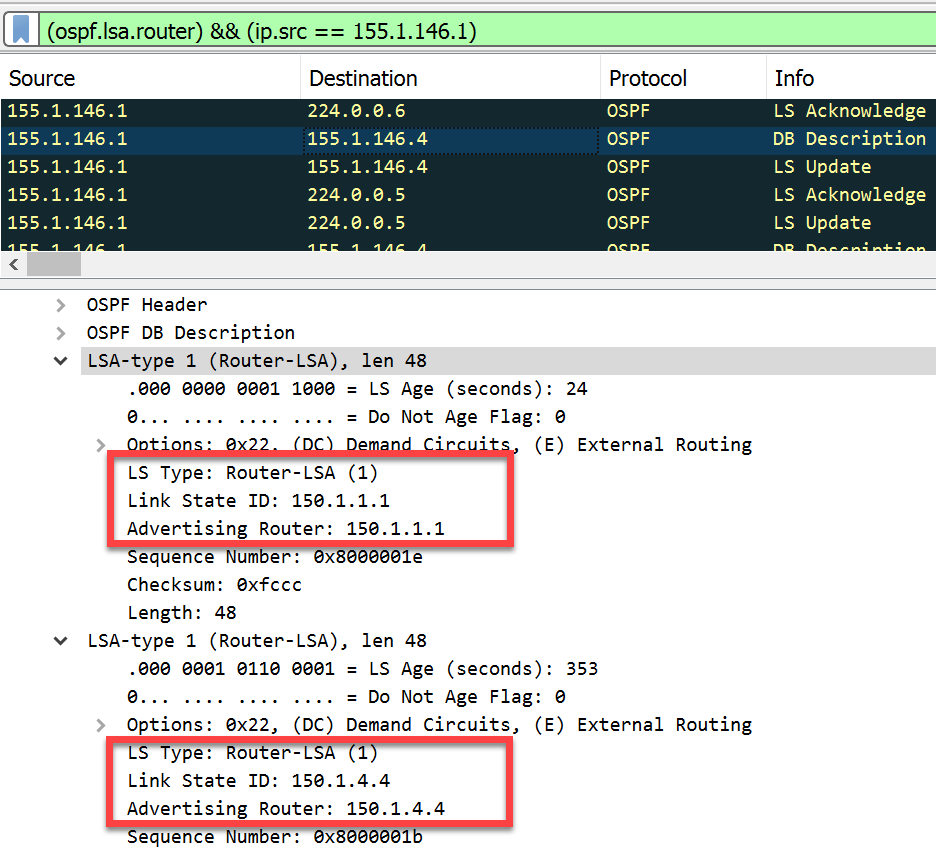
R4
R4#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (150.1.4.4) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
150.1.1.1 150.1.1.1 10 0x80000020 0x00CCFC 2
150.1.4.4 150.1.4.4 9 0x8000001F 0x00EFC5 2
150.1.6.6 150.1.6.6 10 0x8000001E 0x009CC0 1R4#show ip ospf 1 database network
OSPF Router with ID (150.1.4.4) (Process ID 1)
Net Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 1854
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Network Links
Link State ID: 155.1.146.4 (address of Designated Router)
Advertising Router: 150.1.4.4
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x7E07
Length: 36
Network Mask: /24
Attached Router: 150.1.4.4
Attached Router: 150.1.1.1
Attached Router: 150.1.6.6
R6
R6#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (150.1.6.6) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
150.1.1.1 150.1.1.1 10 0x80000020 0x00CCFC 2
150.1.4.4 150.1.4.4 10 0x8000001F 0x00EFC5 2
150.1.6.6 150.1.6.6 9 0x8000001E 0x009CC0 1R6#show ip ospf 1 database network
OSPF Router with ID (150.1.6.6) (Process ID 1)
Net Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 1855
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Network Links
Link State ID: 155.1.146.4 (address of Designated Router)
Advertising Router: 150.1.4.4
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x7E07
Length: 36
Network Mask: /24
Attached Router: 150.1.4.4
Attached Router: 150.1.1.1
Attached Router: 150.1.6.6