TCP Startup Connection Process
- The TCP startup connection process begins with a handshake between two hosts.
- One host initiates the handshake to another host.
- To ensure that the destination host is available.
- To ensure that the destination host is listening on the destination port number.
- Inform the destination host of the initiator’s sequence number so that the two sides can track data as it is transferred.
Step #1
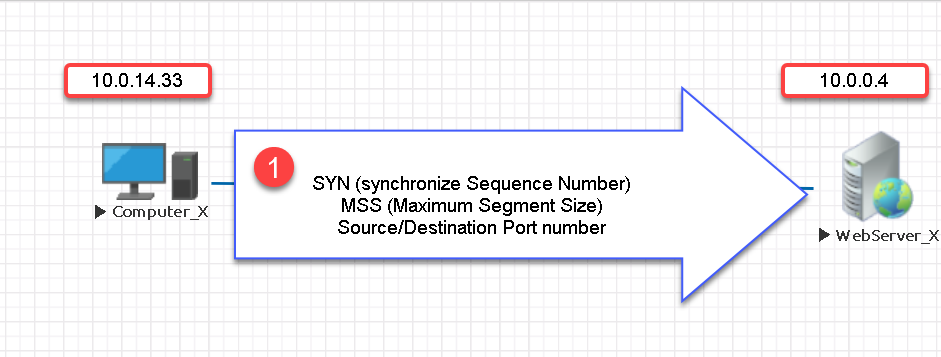
- Computer_X sends a TCP packet to WebServer_X.
- Computer_X initiates a TCP request to WebServer_X on TCP port 2023. Computer_X will use a randomly generated source port.
- The packet does NOT contain any data.
- It contains Computer_X’s starting sequence number indicated by the (SYN) bit number 1.
- The source and destination port numbers.
- Indicating the maximum segment size (MSS) that it can fit into each TCP packet.
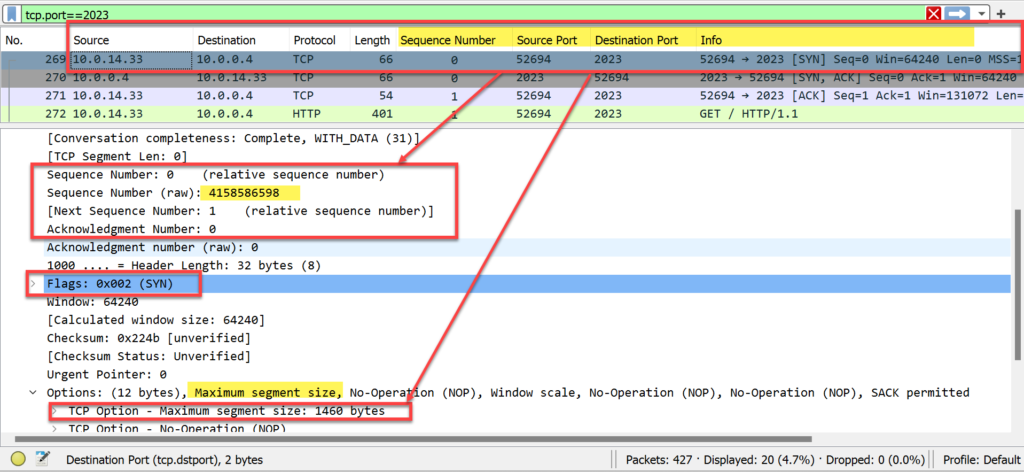
- The sequence # in the SYN packet from Computer_X = 4,158,586,598 (raw) and 0 (relative sequence number).
- The sequence # is used to track the sequence of data sent to WebServer_X and ensure packets are not missing.
- The SYN flag is set to 1. in the flags field.
- As this is the first packet, the acknowledgment # is set to 0.
Step # 2
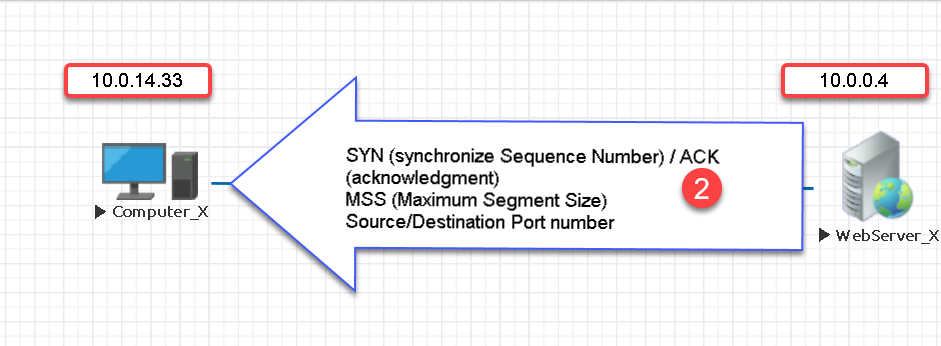
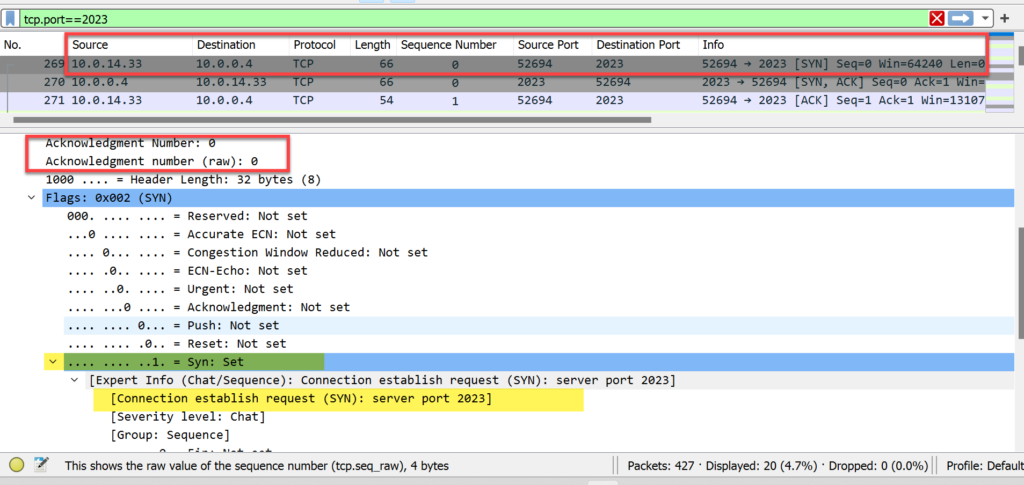
- WebServer_X responds with its starting sequence number indicated by the (SYN) bit setting of 1 in the packet.
- WebServer_X also responds with its maximum segment size (MSS).
- The acknowledgment bit is set to 1 in the reply and acknowledges receipt of the first packet in the three-way handshake.
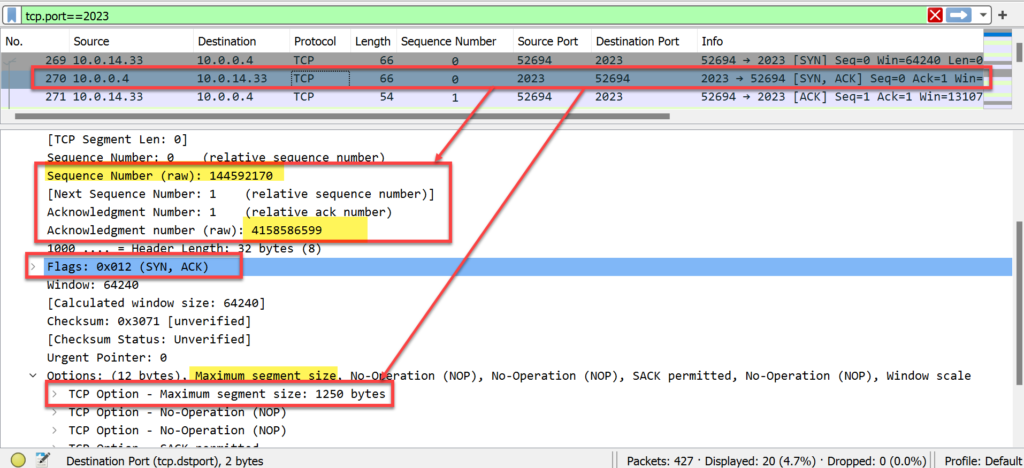
- WebServer_X defined its starting sequence # of 1,445,592,170.
- The acknowledgment # field value is 4,158,586,599, which is the next sequence number that Computer_X expects to receive from WebServer_X.
- The packet has two flags set: SYN and ACK (acknowledging receipt of Computer_X’s first packet).
- This packet also indicates an MSS of 1250 bytes from the host.
Step # 3
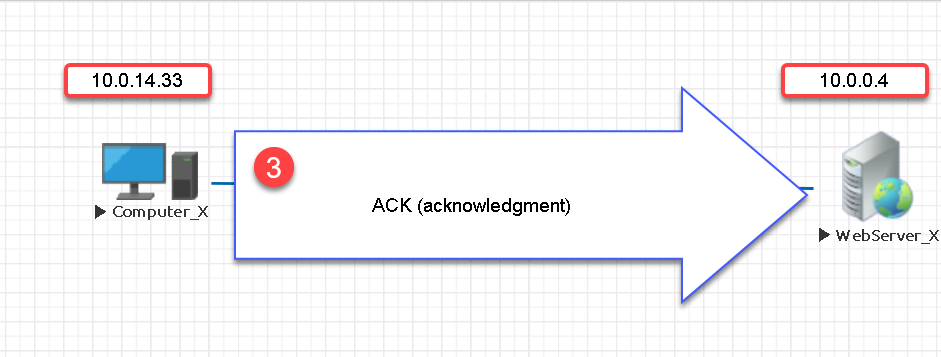
Computer_X acknowledges receipt of WebServer_X’s sequence number and segment size information.
This third packet completes the three-way handshake process.
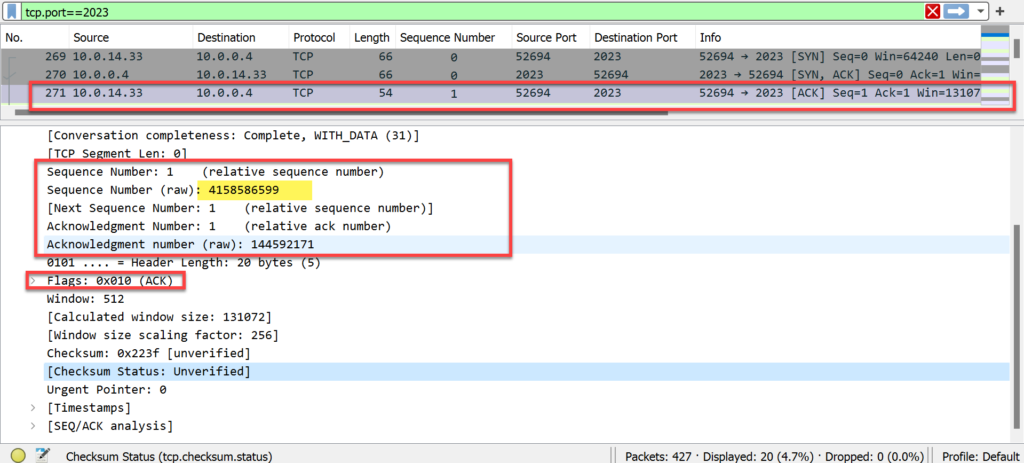
- Computer_X’s sequence # is now 4,158,586,599.
- The acknowledgment # is 1,445,592,171. This indicates that the next expected sequence # from WebServer_X is 1,445,592,171.
- The final packet in the handshake process has the ACK flag set to indicate receipt of WebServer_X’s sequence number.
Note:
- MSS and MTU are often confused with each other.
- MSS is the amount of data that can fit in a packet after the TCP header.
- MTU is the amount of data that can fit inside of a MAC header.
- For example, an Ethernet frame typically has an MTU of 1518 byes.
- The MSS value is 1460.
Ethernet Frame
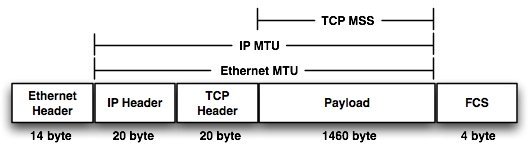
Adding the Ethernet header, IP header, TCP header, Payload, and FCS > 14 + 20 + 20 + 1460 + 4 gives a combined total of 1580
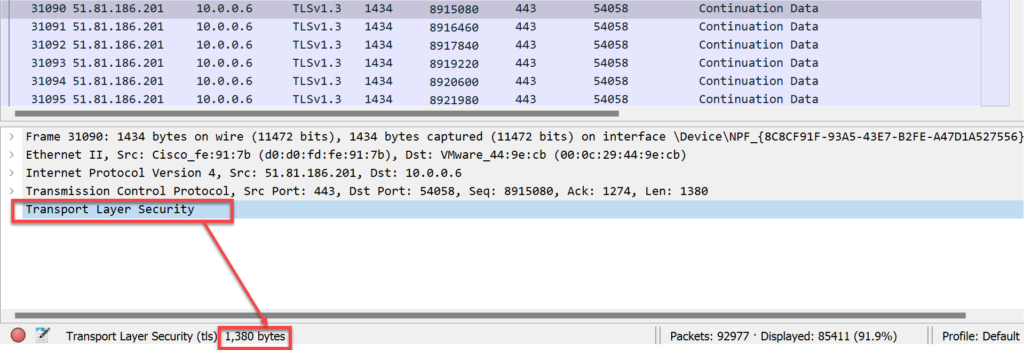
Example Wireshark Packet Capture
- Frame total = 1434 bytes
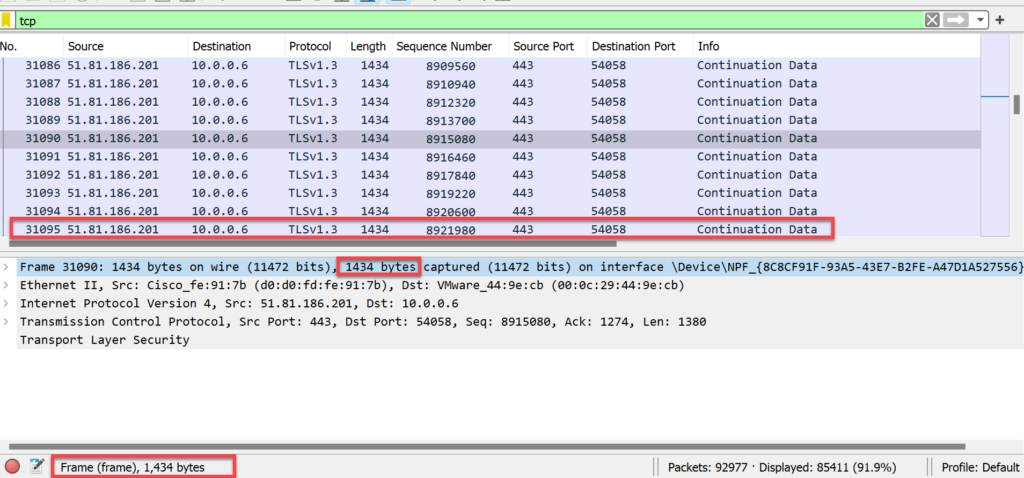
- Ethernet Header total = 14 bytes
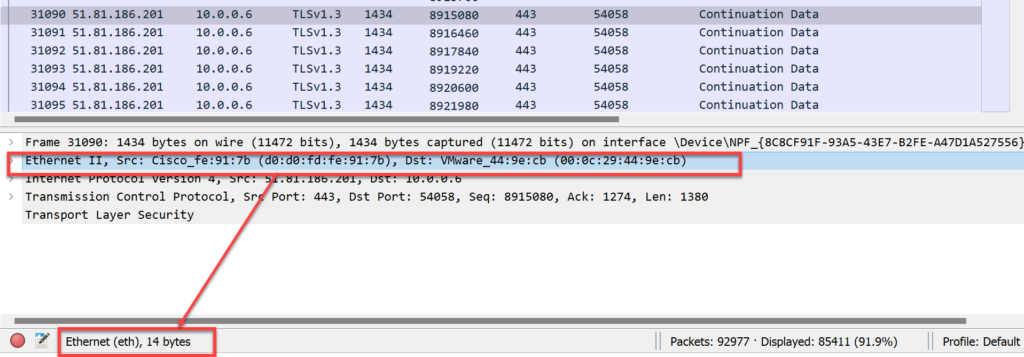
- IP Header
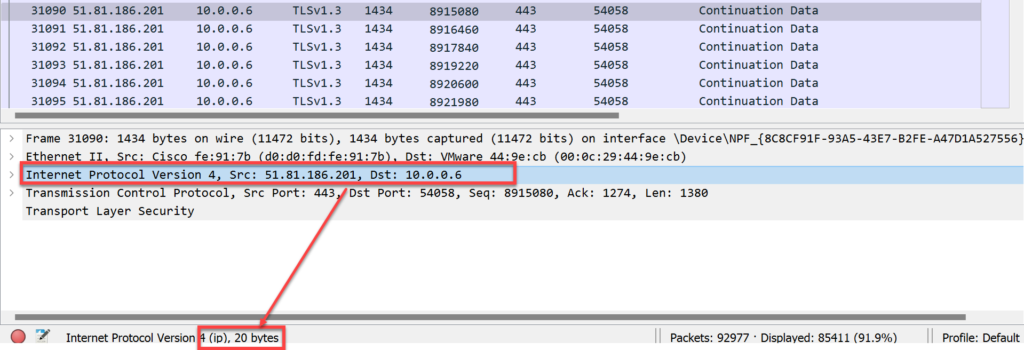
- TCP Header
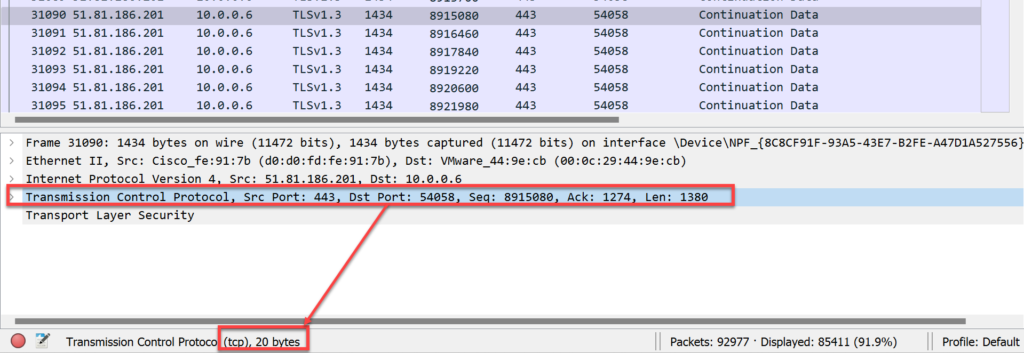
- Pay Load = 1380 bytes