Wireless remote packet capture refers to the process of capturing network traffic on a remote device or network using a wireless connection. This is typically done by using specialized software or tools that can capture network packets and transmit them to a centralized location for analysis.
Remote packet capture can be useful in a variety of scenarios, such as when trying to troubleshoot network issues or monitor network activity from a remote location. By capturing network packets remotely, network administrators and security professionals can gain insight into network performance and identify potential security threats.
There are several tools available for wireless remote packet capture, including Wireshark, tcpdump, and Tshark. These tools allow you to capture network packets and transmit them wirelessly to a centralized location for analysis. Some tools also provide additional features such as filtering and packet decoding, which can help you better understand the data that is being transmitted over the network.
Overall, wireless remote packet capture is a valuable tool for network administrators and security professionals who need to monitor network activity and identify potential security threats.
- Verify that the adapter is online
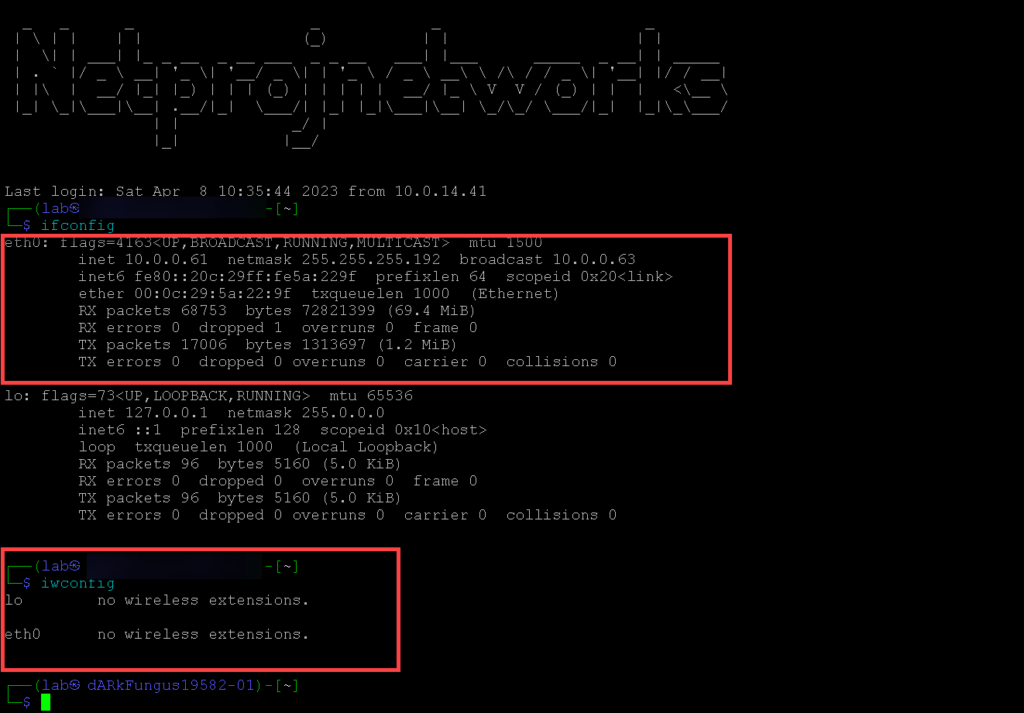
└─$ iwconfig
lo no wireless extensions.
eth0 no wireless extensions.
wlan0 IEEE 802.11 ESSID:off/any
Mode:Managed Access Point: Not-Associated Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry short long limit:2 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
wlan1 IEEE 802.11 ESSID:off/any
Mode:Managed Access Point: Not-Associated Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry short long limit:2 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
2. Use airomon-ng to stop the processes that are running on the adapter
└─$ sudo airmon-ng check kill
Killing these processes:
PID Name
3653 wpa_supplicant3. Put the interface into monitor mode
└─$ sudo airmon-ng start wlan1
[sudo] password for lab:
Found 1 processes that could cause trouble.
Kill them using 'airmon-ng check kill' before putting
the card in monitor mode, they will interfere by changing channels
and sometimes putting the interface back in managed mode
PID Name
3653 wpa_supplicant
PHY Interface Driver Chipset
phy0 wlan0 rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT3572
phy1 wlan1 rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT2870/RT3070
(mac80211 monitor mode vif enabled for [phy1]wlan1 on [phy1]wlan1mon)
(mac80211 station mode vif disabled for [phy1]wlan1)
phy2 wlan2mon rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT2870/RT3070
phy3 wlan3 rtl8814au Realtek Semiconductor Corp. RTL8814AU 802.11a/b/g/n/ac
Verify the status of the adapter.
└─$ iwconfig
lo no wireless extensions.
eth0 no wireless extensions.
wlan0 IEEE 802.11 ESSID:off/any
Mode:Managed Access Point: Not-Associated Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry short long limit:2 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
wlan3 unassociated Nickname:"WIFI@RTL8814AU"
Mode:Monitor Frequency=2.412 GHz Access Point: Not-Associated
Sensitivity:0/0
Retry:off RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality:0 Signal level:0 Noise level:0
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0
wlan2mon IEEE 802.11 Mode:Monitor Frequency:2.437 GHz Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry short long limit:2 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
wlan1mon IEEE 802.11 Mode:Monitor Frequency:2.457 GHz Tx-Power=30 dBm
Retry short long limit:2 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
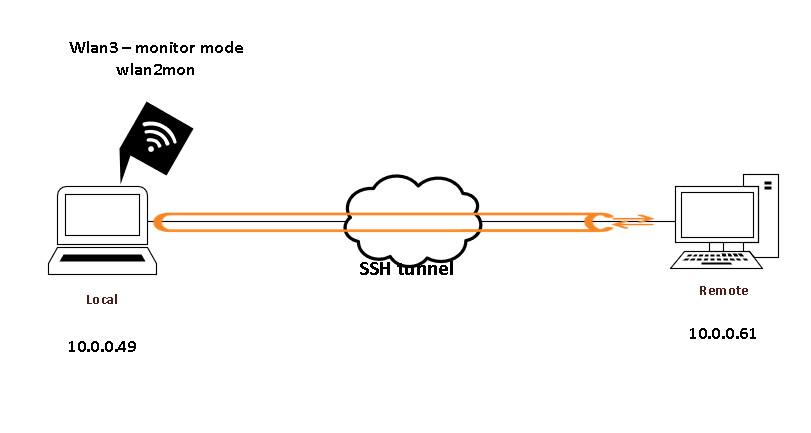
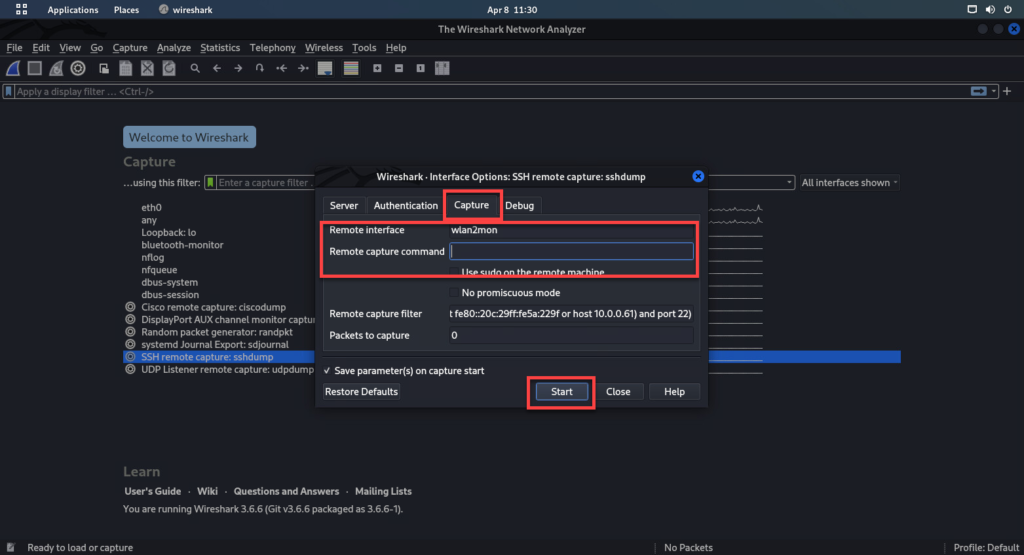
4. Configure the monitor device to send the capture to the remote host
4.a Start wireshark > and run the capture on wlan2mon
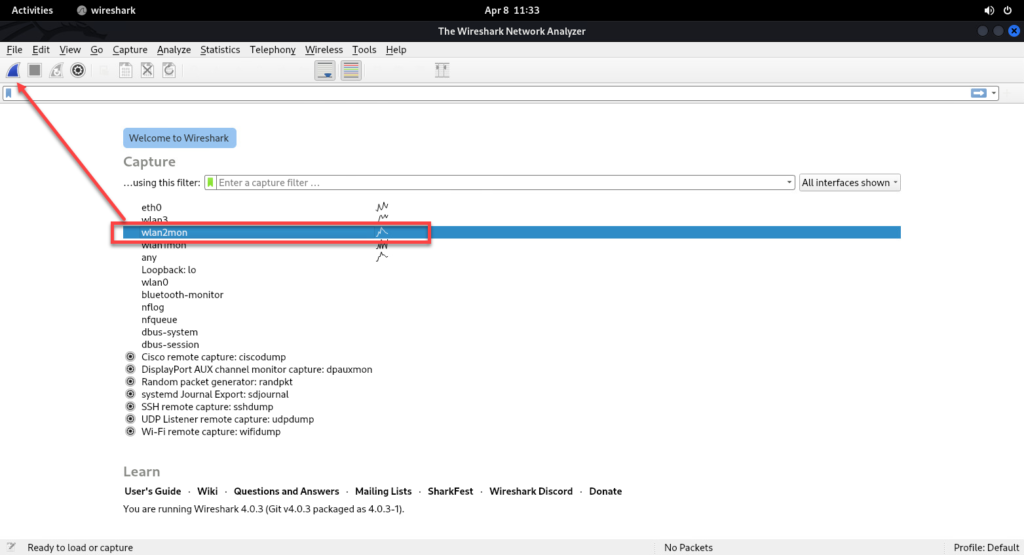
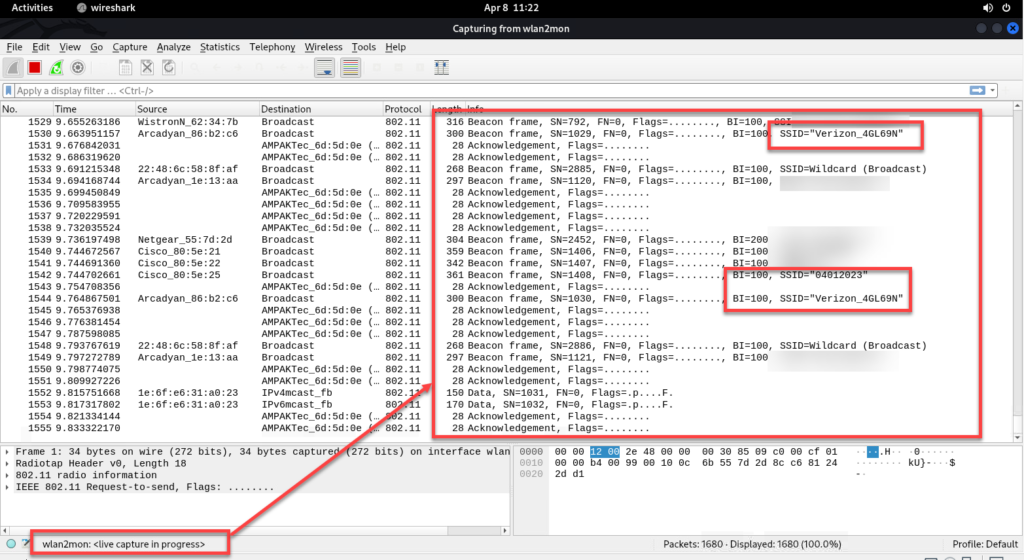
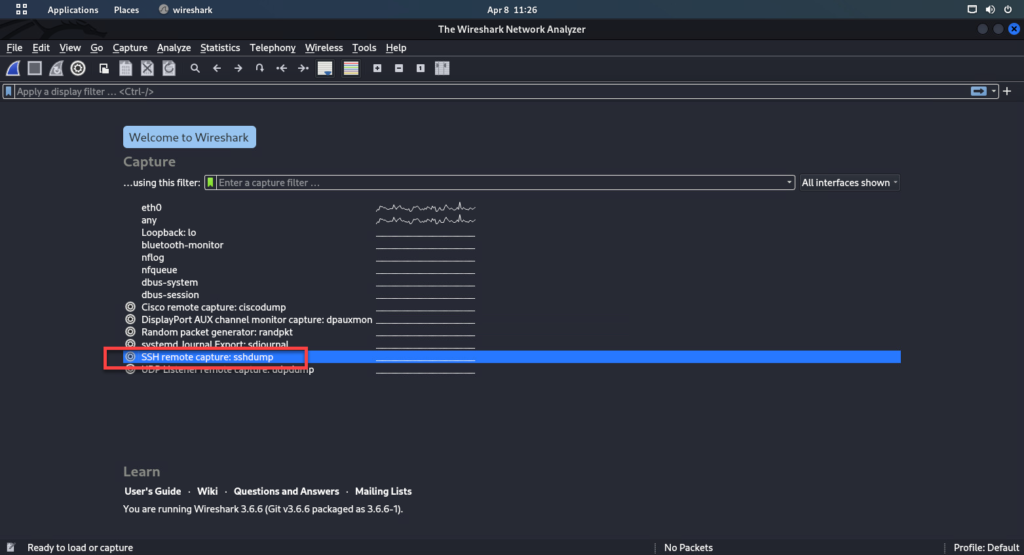
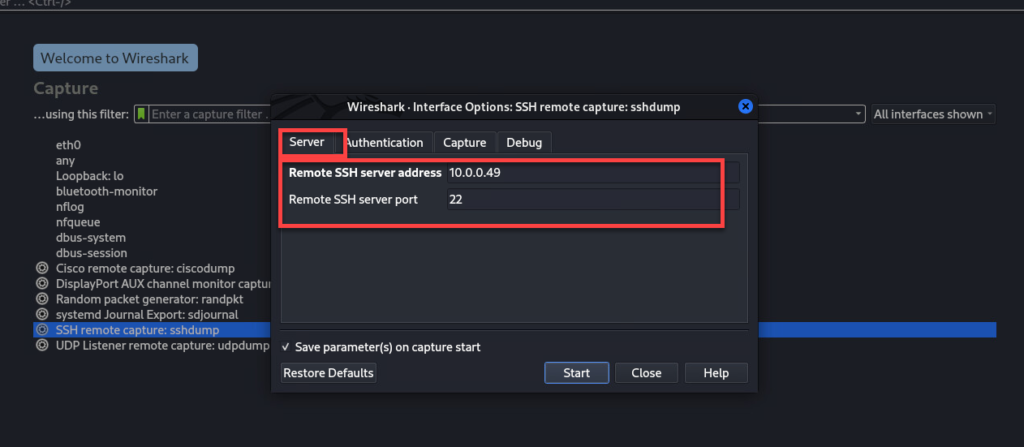
5. Open wireshark on the remote machine and point the remote ssh capture to the other side
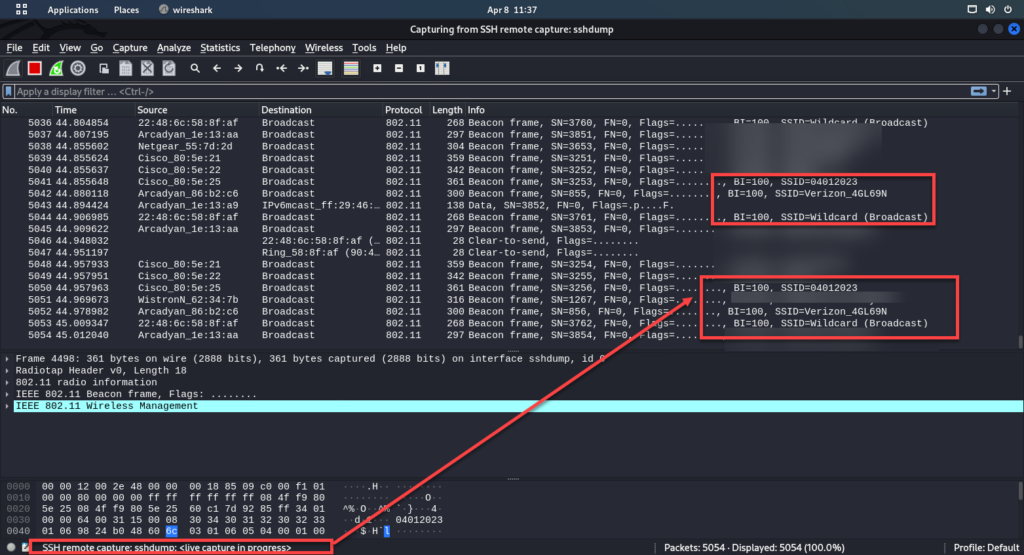
note: The remote device does not have a wireless adapter connected.